First of all, thank you to Bitnami for providing such valuable helm charts to the community. What a great resource!
Why doesn’t Bitnami support adding an SSL redirect for AWS LoadBalancing in their helm charts? I have worked with several lately where the templates baked into the helm charts will not allow the addition of the following ingress section, necessary for automatically redirecting HTTP to HTTPS:
spec:
rules:
- host: example.com
http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: ssl-redirect
port:
name: use-annotation
path: /*
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
- backend:
service:
name: default-service
port:
name: http
path: /*
pathType: ImplementationSpecificThat section of YAML, (in addition to the required annotations), will provision an ALB with listeners on port 80 and 443, with SSL configured, and redirect HTTP to HTTPS.
The fix is not that difficult, but does add one more step to deploying these helm charts. I suspect the preference within Bitnami is for their managed service and the nginx ingress controller, so that might explain a lot here. One hassle with the fix is that you have to always apply a second manifest after installing the helm chart.
To fix the issue, first, deploy the helm chart. This example is using the wordpress helm chart. Here is a custom values.yaml that I used to deploy with:
service:
type: NodePort
ingress:
enabled: true
certManager: false
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
apiVersion: ""
ingressClassName: "alb"
hostname: example.com
path: /*
annotations: {
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: 'alb',
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/certificate-arn: 'arn:aws:acm:us-west-2:**********:certificate/5a0ba7d7-d65c-45f1-ae6b-*************',
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/listen-ports: '[{"HTTP": 80}, {"HTTPS":443}]',
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/scheme: 'internet-facing',
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/actions.ssl-redirect: '{"Type": "redirect", "RedirectConfig": { "Protocol": "HTTPS", "Port": "443", "StatusCode": "HTTP_301"}}'
}
tls: falseNext, install via helm – this assumes the bitnami repo is properly configured via ‘helm add’:
helm install wordpress-test -f values.yaml bitnami/wordpressThen, get the yaml that describes the ingress:
$ kubectl get ingress -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
items:
- apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/actions.ssl-redirect: '{"Type": "redirect", "RedirectConfig":
{ "Protocol": "HTTPS", "Port": "443", "StatusCode": "HTTP_301"}}'
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/certificate-arn: arn:aws:acm:us-west-2:************:certificate/5a0ba7d7-d65c-45f1-ae6b-************
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/listen-ports: '[{"HTTP": 80}, {"HTTPS":443}]'
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/scheme: 'internet-facing'
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: alb
meta.helm.sh/release-name: wordpress-test
meta.helm.sh/release-namespace: default
creationTimestamp: "2021-09-06T19:09:00Z"
finalizers:
- ingress.k8s.aws/resources
generation: 1
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/instance: wordpress-test
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: Helm
app.kubernetes.io/name: wordpress
helm.sh/chart: wordpress-11.0.16
name: wordpress-test
namespace: default
resourceVersion: "2680361"
uid: ***-***-***
spec:
rules:
- host: example.com
http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: wordpress-test
port:
name: http
path: /*
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
status:
loadBalancer:
ingress:
- hostname: internal-k8s-default-***********.us-west-2.elb.amazonaws.com
kind: List
metadata:
resourceVersion: ""
selfLink: ""
Once you have that YAML, create a new file, which will allow us to patch the ingress, using the following format. Be sure to remove the uid, version, and timestamps. Note that the updated section is under spec.rules.http.paths:
apiVersion: v1
items:
- apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/actions.ssl-redirect: '{"Type": "redirect", "RedirectConfig":
{ "Protocol": "HTTPS", "Port": "443", "StatusCode": "HTTP_301"}}'
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/certificate-arn: arn:aws:acm:us-west-2:************:certificate/5a0ba7d7-d65c-45f1-ae6b-************
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/listen-ports: '[{"HTTP": 80}, {"HTTPS":443}]'
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/scheme: 'internet-facing'
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: alb
meta.helm.sh/release-name: wordpress-test
meta.helm.sh/release-namespace: default
finalizers:
- ingress.k8s.aws/resources
generation: 1
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/instance: wordpress-test
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: Helm
app.kubernetes.io/name: wordpress
helm.sh/chart: wordpress-11.0.16
name: wordpress-test
namespace: default
spec:
rules:
- host: example.com
http:
paths:
- path: /*
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
backend:
service:
name: ssl-redirect
port:
name: use-annotation
- path: /*
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
backend:
service:
name: wordpress-test
port:
name: http
status:
loadBalancer:
ingress:
- hostname: internal-k8s-default-***********.us-west-2.elb.amazonaws.com
kind: List
metadata:
resourceVersion: ""
selfLink: ""Once this file has been created, apply the change to the deployed ingress:
> kubectl apply -f ingress-override.yaml
Warning: resource ingresses/wordpress-test is missing the kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration annotation which is required by kubectl apply. kubectl apply should only be used on resources created declaratively by either kubectl create --save-config or kubectl apply. The missing annotation will be patched automatically.
ingress.networking.k8s.io/wordpress-test configuredThere will be a warning because the initial creation of the resource was through helm and not kubectl. To confirm the change, run the command kubectl get ingress -o yaml again. The output should resemble the YAML file, with the exception of the new kubectl metadata.
Now, if the AWS LoadBalancer Controller is running properly, the ALB should have a redirect from HTTP to HTTPS, ie:
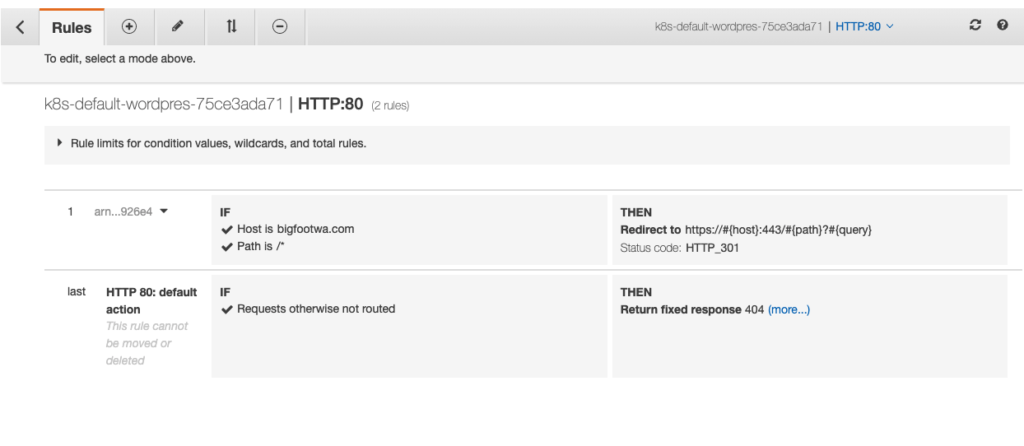
If using terraform / terragrunt, simply apply the manifest using the helm provider, then use kubectl_manifest to apply the ingress updates via template.
Leave a Reply